OctaneRender: A beginner's guide
One of the pioneers of GPU rendering, OctaneRender is a highly regarded, physically accurate render engine for all major platforms.

For a long time unbiased rendering was barely touched by a wide range of render engines. This was because an unbiased render solution was computationally intensive and therefore very slow. This was a great shame, as from a user’s perspective an unbiased rendering solution offered ‘true’ physical lighting exactly as would be seen by the naked eye or the lens of a camera.
OctaneRender from OTOY was one of the pioneers of moving the computationally intensive tasks of unbiased rendering over to the Graphics Processing Unit (GPU, otherwise known as the graphics card), which is able to divide tasks across a much greater number of parallel cores. By using GPUs, all of a sudden unbiased renders could be achieved in minutes on a single machine instead of hours or days – as was the norm before using CPU rendering.
As OctaneRender gets ready for a milestone version 4 release, it has become one of the leading render engines on the market. This is primarily due to the large number of software solutions that OctaneRender can integrate into through the wide selection of plugins that are available for digital content creation applications, including 3ds Max, Maya, Cinema 4D, Houdini, Modo and LightWave to name but a few.
OctaneRender is available for CAD applications and also Nuke, allowing compositors to work with OctaneRender without needing to round-trip to an application. A lot of this flexibility is handled in the background by the ORBX format, which OTOY uses as the underpinnings of its standalone application, and makes transferring scenes between applications easier than it would be with other render solutions.
OctaneRender also has one of the most responsive render preview systems, making iterative changes easy to visualise in near real time. As OctaneRender is an unbiased solution, it is easy for artists new to 3D to learn with OctaneRender materials, lighting and cameras all corresponding to real-world settings. Here are some key features that will help you get to grips with this powerful software.
01. Standalone application

Unlike many other third-party render solutions, OctaneRender comes with its own standalone application. This may initially seem odd, as so much time is spent in the host application with the chosen OctaneRender plugin. However, having a standalone application is a really useful tool because it allows a wide range of elements to be tested as scenes are moved between different creation applications.
02. Render preview
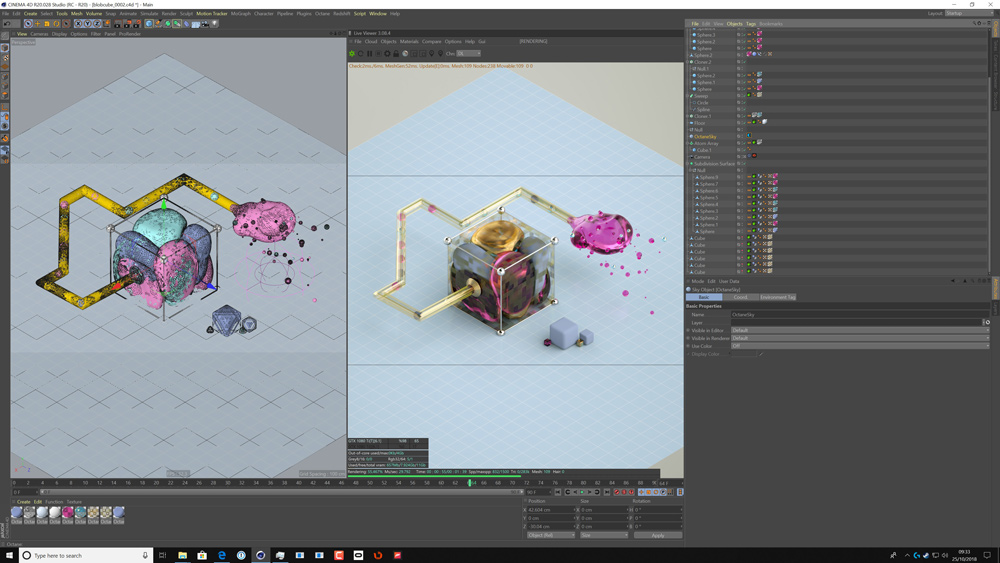
OctaneRender has one of the most impressive render preview windows in the digital content space. Not only is it exceptionally responsive in comparison to other GPU render solutions, OctaneRender allows – depending on the plugin – quick access to material selection, focus point selection and AOV/render layer preview. Support is being implemented for Apple Metal allowing Mac users to bring OctaneRender into their workflows.
Get the Creative Bloq Newsletter
Daily design news, reviews, how-tos and more, as picked by the editors.
03. For compositors
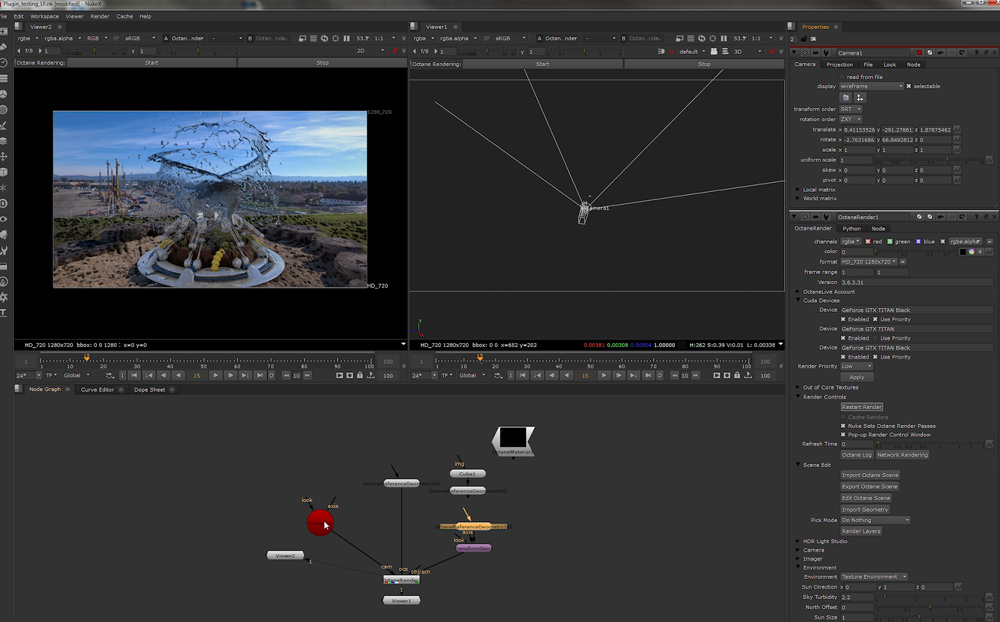
OctaneRender is friendly for compositors as it is available as a plugin for the compositing application Nuke which supports deep pixel rendering, allowing Nuke artists to have access to the latest compositing toolsets combined with the speed of GPU rendering. As OctaneRender also supports features such as volumetric rendering, it is an excellent solution for effects work where dust, smoke or flames are often required.
04. Material library
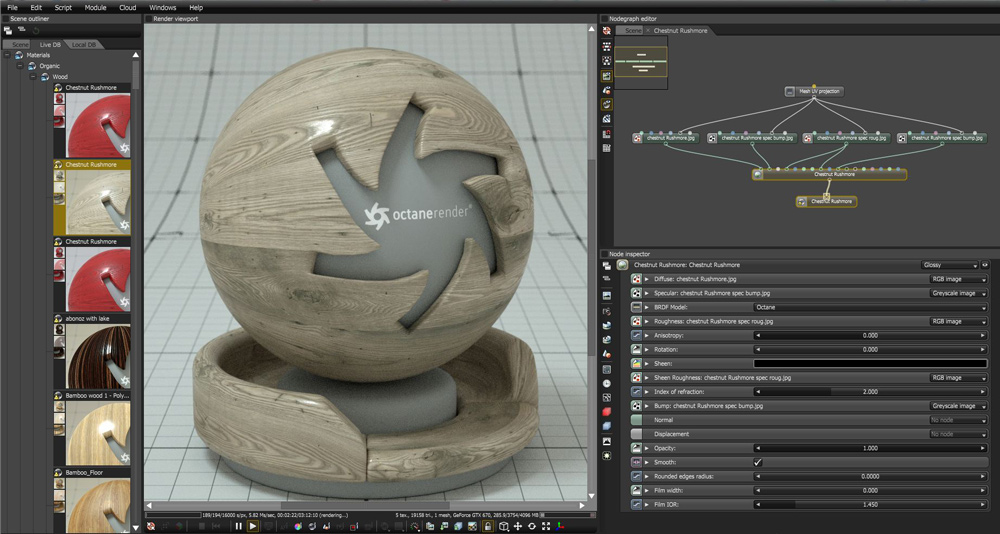
OctaneRender comes with an array of materials that are constantly added to by the community, and are easily accessed in host applications through the OctaneRender LiveDB. As OctaneRender is an unbiased render engine, materials have a logic to them that is easier to grasp for new 3D artists than those of a biased render engine. OctaneRender also supports a full material baking paradigm, making it an excellent tool for those working in real-time creation.
05. Nodes in OctaneRender

Nodal workflows are key to the power of OctaneRender. Nodes are used to control practically every aspect of the application in the standalone version and they are also used through the OctaneRender plugin environments for materials. Although these are potentially confusing at first for artists new to nodal workflows, nodes can offer great efficiencies, especially when using texture files and gradients that need only one node to control multiple outputs.
06. OctaneRender 4

The new release – OctaneRender 4 – is already available as a beta to existing customers. Major highlights are the integration of OTOY’s real-time path-tracing engine, Brigade, into OctaneRender. There is also the addition of a Spectral AI Denoiser and AI Light system that will enable cleaner animations and dramatically faster render times, improved fog and a new planetary environment. OctaneRender 3 full-licence customers will get a free upgrade to the new version.
This article originally appeared in 3D World issue 242; subscribe here.
Read more:

Thank you for reading 5 articles this month* Join now for unlimited access
Enjoy your first month for just £1 / $1 / €1
*Read 5 free articles per month without a subscription

Join now for unlimited access
Try first month for just £1 / $1 / €1

Mike Griggs is a veteran digital content creator and technical writer. For nearly 30 years, Mike has been creating digital artwork, animations and VR elements for multi-national companies and world-class museums. Mike has been a writer for 3D World Magazine and Creative Bloq for over 10 years, where he has shared his passion for demystifying the process of digital content creation.
